Definition
A stent is a tiny tube placed into a hollow structure in your body. This structure can be an artery, a vein, or another structure, such as the tube that carries urine (ureter). The stent holds the structure open.
Alternative Names
Drug-eluting stents; Urinary or ureteral stents; Coronary stents
Description
When a stent is placed into the body, the procedure is called stenting. There are different kinds of stents. Most are made of a metal or plastic mesh-like material. However, stent grafts are made of fabric. They are used in larger arteries.
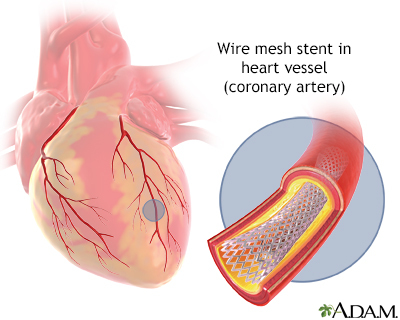
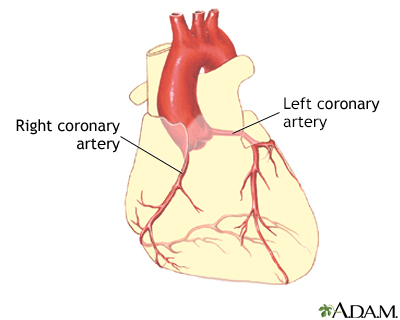
A coronary artery stent is a small, self-expanding, metal mesh tube. It is placed inside a coronary artery after balloon angioplasty. This stent prevents the artery from re-closing.
A drug-eluting stent is coated with a medicine. This medicine helps further prevent the arteries from re-closing. Like other coronary artery stents, it is left permanently in the artery.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Most of the time, stents are used when arteries become narrow or blocked.
Stents are commonly used to treat the following conditions that result from blocked or damaged blood vessels:
Other reasons to use stents include:
References
Tambyraja AL. Vascular and endovascular surgery. In: Garden OJ, Parks RW, Wigmore SJ, eds. Principles and Practice of Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 22.
Teirstein PS. Interventional and surgical treatment of coronary artery disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 65.
Textor SC. Renovascular hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 47.
White CJ. Atherosclerotic peripheral arterial disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 71.