Vaginitis test - wet mount
Definition
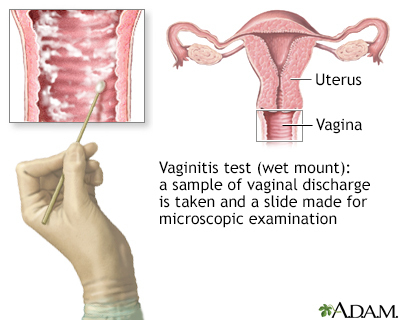
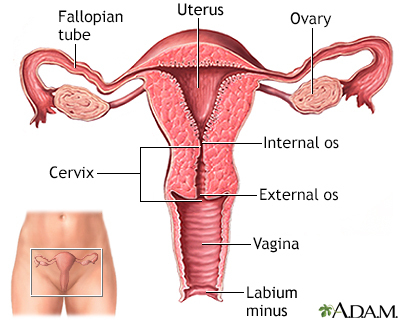
The vaginitis wet mount test is a test to detect an infection of the vagina.
Alternative Names
Wet prep - vaginitis; Vaginosis - wet mount; Trichomoniasis - wet mount; Vaginal candida - wet mount
How the Test is Performed
This test is done in your health care provider's office.
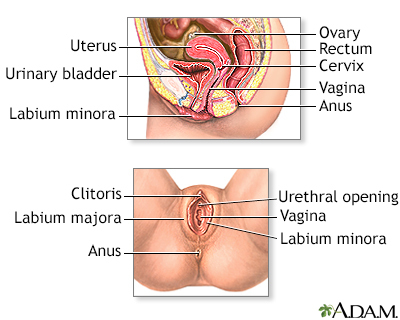
- You lie on your back on the exam table. Your feet are supported by footrests.
- The provider gently inserts an instrument (speculum) into the vagina to hold it open and view inside.
- A sterile, moist cotton swab is gently inserted into the vagina to take a sample of discharge.
- The swab and speculum are removed.
The discharge is sent to a lab. There, it is placed onto a slide. It is then viewed under a microscope and checked for signs of infection.
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow any instructions from your provider on preparing for the test. This may include:
- In the 2 days before the test, do not use creams or other medicines in the vagina.
- Do not douche. (You should never douche. Douching can cause infection of the vagina or uterus.)
How the Test will Feel
There may be slight discomfort when the speculum is inserted into the vagina.
Why the Test is Performed
The test looks for the cause of vaginal irritation and discharge.
Normal Results
A normal test result means there are no signs of an infection.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results mean there is an infection. The most common infections are due to one or a combination of the following:
- Bacterial vaginosis. Bacteria that normally live in the vagina overgrow, causing a heavy, white, fishy-smelling discharge and possibly a rash, painful intercourse, or odor after intercourse.
- Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted disease.
- Vaginal yeast infection.
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
Gallery
References
Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Plourde AR, Beavis KG. Specimen collection and handling for diagnosis of infectious diseases. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 66.