Three Warning Signs of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men and eighth most common cancer in women, affecting about 80,000 people in the United States every year.…

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
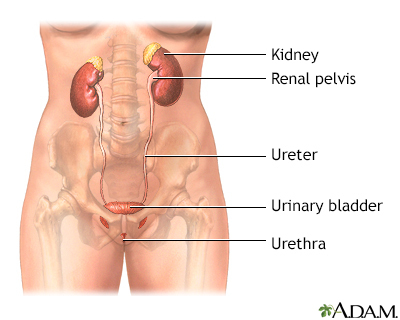
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds that pass through the urine.
Urine appearance and color; Routine urine test; Cystitis - urinalysis; Bladder infection - urinalysis; UTI - urinalysis; Urinary tract infection - urinalysis; Hematuria - urinalysis
A urine sample is needed. Your health care provider will tell you what type of urine sample is needed. Two common methods of collecting urine are 24-hour urine collection and clean catch urine specimen.
The sample is sent to a lab, where it is examined for the following:
PHYSICAL COLOR AND APPEARANCE
How the urine sample looks to the naked eye:
MICROSCOPIC APPEARANCE
The urine sample is examined under a microscope to:
CHEMICAL APPEARANCE (urine chemistry)
Examples of specific urinalysis tests that may be done to check for problems include:
Certain medicines change the color of urine, but this is not a sign of disease. Your provider may tell you to stop taking any medicines that can affect test results.
Medicines that can change your urine color include:
The test involves only normal urination, and there is no discomfort.
A urinalysis may be done:
Normal urine varies in color from almost colorless to dark yellow. Some foods, such as beets and blackberries, may turn urine red.
Usually, glucose, ketones, protein, and bilirubin are not detectable in urine. The following are not normally found in urine:
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
Abnormal results may mean you have an illness, such as:
Your provider can discuss the results with you.
There are no risks with this test.
If a home test is used, the person reading the results must be able to tell the difference between colors, because the results are interpreted using a color chart.
Chernecky CC, Berger BJ. Urinalysis (UA) - urine. In: Chernecky CC, Berger BJ, eds. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:1146-1148.
Riley RS, McPherson RA. Basic examination of urine. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
Sobel JD, Brown P. Urinary tract infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 72.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men and eighth most common cancer in women, affecting about 80,000 people in the United States every year.…

Chronic kidney disease doesn’t always come with warning signs or symptoms. To one University of Florida Health physician, it is a silent killer. March 11 is…