Highest-ranked Pediatric Neurosurgery & Neurology program in North Florida.

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
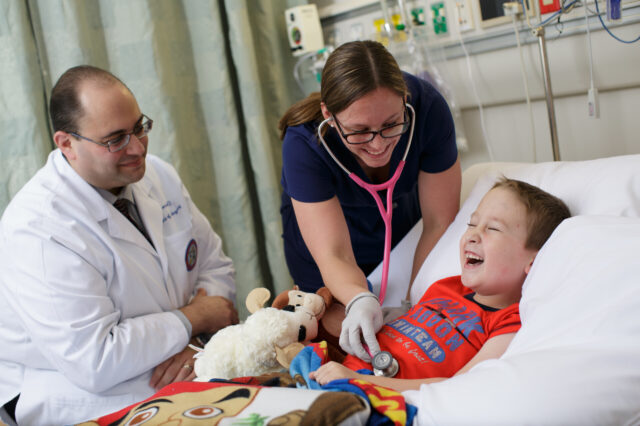
From the most complex brain and spinal disorders requiring the most challenging interventions to more common conditions and procedures, our expert team of pediatric neurosurgeons and neurosurgery nurse practitioners offers the complete spectrum of multidisciplinary care.
In close collaboration with UF Health Shands Children’s Hospital, nationally ranked in four pediatric programs, we care for patients from birth to age 21, and select adults with congenital neurological disorders. We provide initial consultation, surgery and continued post-operative care. Our neurosurgeons and nurse practitioners have all received advanced pediatric training, which is crucial in caring for the unique needs of children and adolescents.
We are proud to be the top pediatric neurology and neurosurgery program in North Florida, according to the US News Best Children’s Hospitals rankings. Our highest honor is hearing what our patients are saying and seeing them do well.
Our specialty programs include the treatment of the following conditions:
See a complete list of our conditions and treatments.
Our neurosurgeons operate in leading-edge pediatric operating rooms. The University of Florida in Gainesville is equipped with advanced technologies such as intraoperative MRI, sophisticated neurosurgical microscope and endoscope systems, hybrid operating rooms, stereotactic navigation, neurophysiologic monitoring, ultrasound, stereoelectroencephalography, a neurosurgical robot, and a minimally invasive laser. All of these decrease the probability of multiple operations, allow minimally invasive procedures whenever possible, increase overall surgical success, minimize pain, and promote faster recovery.
Highest-ranked Pediatric Neurosurgery & Neurology program in North Florida.

UF Health Shands Children’s Hospital ranks among the nation’s top hospitals in four specialties.

Our pediatric neurosurgeons can perform the most advanced surgical techniques possible in our leading-edge operating rooms. Equipped with leading-edge technology, our surgeons can see deep into the brain in the most minimally-invasive ways possible.
Our staff leverages pediatric intraoperative MRI (iMRI) to obtain precise pictures of the brain, which guide neurosurgeons in removing brain tumors and other abnormalities during neurosurgery.
Real-time images of the brain during a procedure help the neurosurgery team to immediately determine more precisely if they have successfully removed brain tumors and other abnormalities, versus having to wait for a follow-up MRI and possible additional surgery. This level of accuracy with the most technically advanced equipment helps us provide the best possible outcomes for our patients.
Hybrid ORs enable surgical teams to accommodate several different procedures simultaneously. Patients with complex conditions do not need to be transported to different locations to undergo lifesaving surgeries or advanced imaging, such as angiography.
One of the major advances in modern neurosurgery is the use of the neuroendoscope, a slender rod with a lens in it that is attached to a camera and allows a neurosurgeon to clearly see and operate upon deep regions of the brain with minimal disruption of surrounding areas. Neuroendoscopes are frequently used during minimally invasive hydrocephalus, craniosynostosis, tumor, and skull base surgeries.
Another crucial device is the computerized navigation system which helps our neurosurgeons precisely target brain regions using virtual 3D models made from the patient’s imaging. This can be combined with intraoperative ultrasound which uses sound waves to create real-time pictures of the inside of the brain and spinal cord on a computer monitor.
For a patient with epilepsy whose seizures don’t respond to medicine or other treatments, our team of surgeons can pinpoint the source of the patient’s seizures in his or her brain using stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG). SEEG is a procedure that uses sophisticated technology to implant electrodes into the brain through tiny holes in the skull. The electrodes monitor seizure activity. A precision neurosurgical robot often aids electrode placement.
Using the iMRI and navigation systems, our neurosurgeons can offer minimally invasive laser ablation. A thin catheter is carefully placed through a small opening with its tip precisely targeted to an area of abnormal brain, for example, certain tumors or seizure generators. Laser energy is then applied to destroy the area using heat, while the iMRI monitors the temperature of surrounding normal brain regions to protect them.
The neurosurgery team also works closely with the intraoperative neuromonitoring team for operations that involve the most sensitive portions of the brain and spinal cord. Throughout the surgery, the function of the patient’s nerve pathways is being monitored on a computer to maximize the safety of the procedure.
Our technologically advanced and fully-equipped operating rooms enable our staff to guarantee each patient receives the best treatment for his or her brain or spine condition.
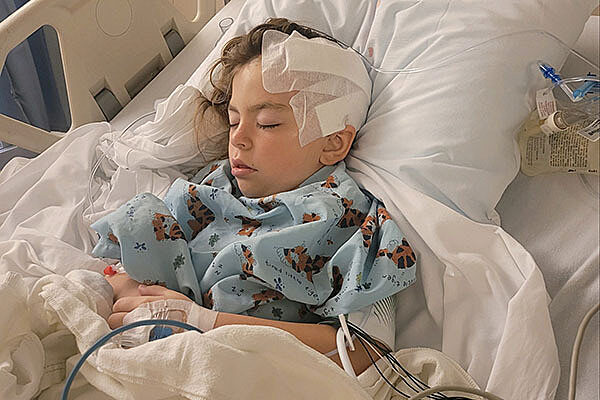
"We want to thank Dr. Governale and his team from the bottom of our hearts for treating Luke and educating us. ‘Thank You’ you will never be enough.” – Megan G.

At UF Health Shands Children’s Hospital, every child diagnosed with a condition requiring neurosurgical expertise is cared for with an individualized treatment plan. We see patients within just a few days for non-emergency cases and within 24 hours for urgent cases.
















Phone number:
(352) 273-6990Address:
755 State Road 47

Taylor Green gazes across his favorite place in the world, scanning the top of Lake Panasoffkee’s spring-fed water. But, in many ways, this 20-year-old pro…

It was a typical March evening in Florida. The Stone family’s six children were playing outside, bouncing on their trampoline and enjoying the extra daylight…