Definition
A secondary infection is an infection that occurs during or after treatment for another infection. It may be caused by the first treatment or by changes in the immune system.
Two examples of a secondary infection are:
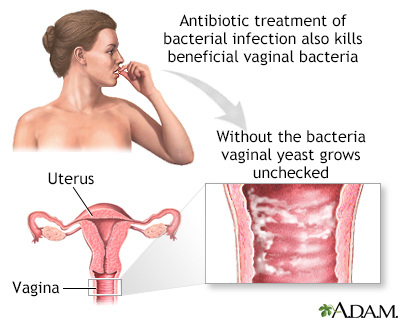
- A vaginal yeast infection after taking antibiotics to treat an infection caused by bacteria
- Pneumonia caused by bacteria or fungi after having an upper respiratory infection (like a cold) that was caused by a virus
References
Dockrell DH, Sundar S, Angus BJ. Infectious disease. In: Ralston SH, Penman ID, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 11.
Reid PT, Innes JA. Respiratory disease. In: Ralston SH, Penman ID, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 17.