Pancreatic abscess
Definition
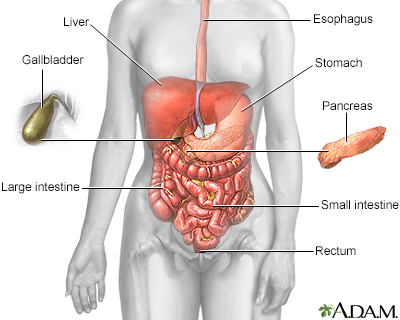
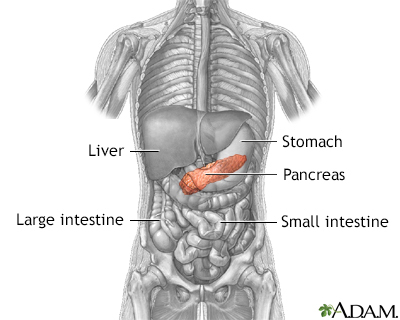
A pancreatic abscess is an area filled with pus within the pancreas.
Causes
Pancreatic abscesses develop in people who have:
- Pancreatic pseudocysts
- Severe pancreatitis that becomes infected
Exams and Tests
Most people with pancreatic abscesses have had pancreatitis. However, the complication often takes 7 or more days to develop.
Signs of an abscess can be seen on:
- CT scan of the abdomen
- MRI of the abdomen
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
Blood culture will show high white blood cell count.
Treatment
It may be possible to drain the abscess through the skin (percutaneous). Abscess drainage can be done through an endoscope using endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) in some cases. Surgery to drain the abscess and remove dead tissue is often needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on how severe the infection is. The death rate from undrained pancreatic abscesses is very high.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have:
- Abdominal pain with fever
- Other signs of a pancreatic abscess, especially if you have recently had a pancreatic pseudocyst or pancreatitis
Prevention
Draining a pancreatic pseudocyst may help prevent some cases of pancreatic abscess. However, in many cases, the disorder is not preventable.
Gallery
References
Barshak MB. Pancreatic infection. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 76.
Forsmark CE. Pancreatitis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 135.
Law R, Baron TH. Endoscopic treatment of pancreatic disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 61.
Van Buren G, Fisher WE. Acute and chronic pancreatitis. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2022. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:169-176.
