Definition
Nearly two out of every three adults in the United States is overweight.
Experts often rely on a formula called the body mass index (BMI) to determine if a person is overweight. The BMI estimates your level of body fat based on your height and weight.
- A BMI from 18.5 to 24.9 is considered normal.
- Adults with a BMI of 25 to 29.9 are considered overweight. Since the BMI is an estimate, it is not accurate for all people. Some people in this group, such as athletes, may have a lot of muscle weight, and therefore not as much fat. These people will not have an increased risk of health problems due to their weight.
- Adults with a BMI of 30 to 39.9 are considered obese.
- Adults with a BMI greater than or equal to 40 are considered extremely obese.
- Anyone more than 100 pounds overweight is considered morbidly obese.
The risk of many medical problems is higher for adults who have excess body fat and fall into the overweight groups.
Changing your lifetstyle
An active lifestyle and plenty of exercise, along with healthy eating, is the safest way to lose weight. Even modest weight loss can improve your health. Get support from family and friends.
Your main goal should be to learn new, healthy ways of eating and make them part of your daily routine.
Many people find it hard to change their eating habits and behaviors. You may have practiced some habits for so long that you may not even know they are unhealthy, or you do them without thinking. You need to be motivated to make lifestyle changes. Make the behavior change part of your life over the long term. Know that it takes time to make and keep a change in your lifestyle.
Work with your health care provider and dietitian to set realistic and safe daily calorie counts that help you lose weight. Keep in mind that if you drop pounds slowly and steadily, you are more likely to keep them off. Your dietitian can teach you about:
- Shopping for healthy foods
- How to read nutrition labels
- Healthy snacks
- Portion sizes
- Sweetened drinks
References
Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apvian CM, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation. 2014;129:S102-S138.
Klein S, Fabbrini E, Romijn JA. Obesity. In: Melmed S, Polonsky KS, Larsen PR, Kronenberg HM, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:chap 36.
 Different types of weight gain
Different types of weight gain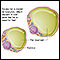 Lipocytes (fat cells)
Lipocytes (fat cells)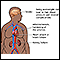 Obesity and health
Obesity and health
