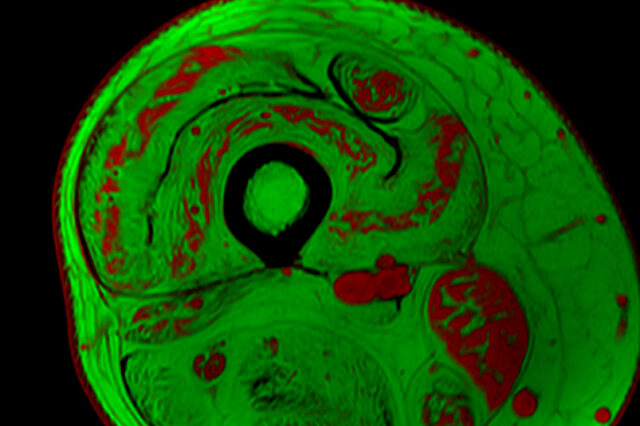
New University of Florida project uses AI to improve treatments for childhood muscular dystrophy
December 6, 2023
A project led by a researcher in the University of Florida's College of Public Health and Health Professions seeks to improve the effectiveness of clinical…
AI at UF, College of Medicine, College of Pharmacy, +2 more