Mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Definition
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) is a rare disease in which the body is missing or does not have enough of an enzyme needed to break down long chains of sugar molecules. These chains of molecules are called glycosaminoglycans (formerly called mucopolysaccharides). As a result, the molecules build up in different parts of the body and cause various health problems.
The condition belongs to a group of diseases called mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs). MPS I is the most common.
There are several other types of MPSs, including:
Alternative Names
Alpha-L-iduronate deficiency; Mucopolysaccharidosis type I; Severe MPS I; Attenuated MPS I; MPS I H; MPS I S; Hurler syndrome; Scheie syndrome; Hurler-Scheie syndrome; MPS 1 H/S; Lysosomal storage disease - mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Causes
MPS I is inherited, which means that your parents must pass the disease on to you. If both parents carry a nonworking copy of the gene related to this condition, each of their children has a 25% (1 in 4) chance of developing the disease.
People with MPS I do not make an enzyme called lysosomal alpha-L-iduronidase. This enzyme helps break down long chains of sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans. These molecules are found throughout the body, often in mucus and in fluid around the joints.
Without the enzyme, glycosaminoglycans build up and damage organs, including the heart. Symptoms can range from mild to severe. The mild form is called attenuated MPS I and the severe form is called severe MPS I.
Symptoms
Symptoms of MPS I most often appear between ages 3 to 8. Children with severe MPS I develop symptoms earlier than those with the less severe form.
Some of the symptoms include:
- Abnormal bones in the spine
- Inability to fully open the fingers (claw hand)
- Cloudy corneas
- Deafness
- Halted growth
- Heart valve problems
- Joint disease, including stiffness
- Intellectual disability that gets worse over time in severe MPS I
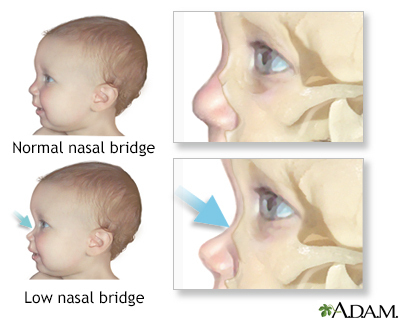
- Thick, coarse facial features with low nasal bridge
Exams and Tests
In some states, babies are tested for MPS I as part of the newborn screening tests.
Other tests that may be done depending on symptoms include:
- ECG
- Genetic testing for changes to the alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA) gene
- Urine tests for extra mucopolysaccharides
- X-ray of the spine
Treatment
Enzyme replacement therapy may be recommended. The medicine, called laronidase (Aldurazyme), is given through a vein (IV, intravenously). It replaces the missing enzyme. Talk to your child's provider for more information.
Bone marrow transplant has been tried. The treatment has had mixed results.
Other treatments depend on the organs that are affected.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with MPS I and their families can be found at:
- National MPS Society -- mpssociety.org/
- National Organization for Rare Disorders -- rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/mucopolysaccharidosis-type-i/
- NIH Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center -- rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10335/mucopolysaccharidosis-type-i
Outlook (Prognosis)
Children with severe MPS I usually do not do well. Their health problems worsen over time, resulting in death by age 10.
Children with attenuated (milder) MPS I have fewer health problems, with many leading fairly normal lives into adulthood.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
- You have a family history of MPS I and are considering having children
- Your child begins to show symptoms of MPS I
Prevention
Experts recommend genetic counseling and testing for couples with a family history of MPS I who are considering having children. Prenatal testing is available.
Gallery
References
Pyeritz RE. Inherited diseases of connective tissue. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 244.
Spranger JW. Mucopolysaccharidoses. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 107.
Turnpenny PD, Ellard S, Cleaver R. Inborn errors of metabolism. In: Turnpenny PD, Ellard S, Cleaver R, eds. Emery's Elements of Medical Genetics and Genomics. 16th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.