Hemolytic transfusion reaction
Definition
A hemolytic transfusion reaction is a serious complication that can occur after a blood transfusion. The reaction occurs when the red blood cells that were given during the transfusion are destroyed by the person's immune system. When red blood cells are destroyed, the process is called hemolysis.
There are other types of allergic transfusion reactions that do not cause hemolysis.
Alternative Names
Blood transfusion reaction
Causes
Blood is classified into four different types: A, B, AB, and O.
Another way blood cells may be classified is by Rh factors. People who have Rh factors in their blood are called "Rh positive." People without these factors are called "Rh negative." Rh negative people form antibodies against Rh factor if they receive Rh positive blood.
There are also other factors to identify blood cells, in addition to ABO and Rh.
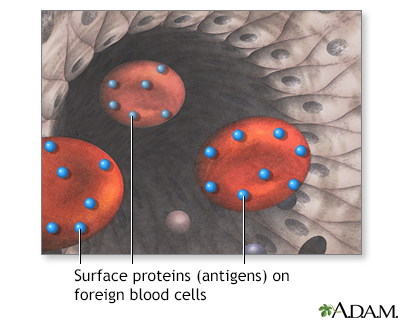
Your immune system can usually tell its own blood cells from those of another person. If you receive blood that is not compatible with your blood, your body produces antibodies to destroy the donor's blood cells. This process causes the transfusion reaction. Blood that you receive in a transfusion must be compatible with your own blood. This means that your body does not have antibodies against the blood you receive.
Most of the time, a blood transfusion between compatible groups (such as O+ to O+) does not cause a problem. Blood transfusions between incompatible groups (such as A+ to O-) cause an immune response. This can lead to a serious transfusion reaction. The immune system attacks the donated blood cells, causing them to burst.
Today, all blood is carefully screened. Transfusion reactions are rare.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Back pain
- Bloody urine
- Chills
- Fainting or dizziness
- Fever
- Flank pain
- Flushing of the skin
Symptoms of a hemolytic transfusion reaction most often appear during or right after the transfusion. Sometimes, they may develop after several days (delayed reaction).
Exams and Tests
This disease may change the results of these tests:
Treatment
If symptoms occur during the transfusion, the transfusion must be stopped right away. Blood samples from the recipient (person getting the transfusion) and from the donor may be tested to tell whether symptoms are being caused by a transfusion reaction.
Mild symptoms may be treated with:
- Acetaminophen, a pain reliever to reduce fever and discomfort
- Fluids given through a vein (intravenous) and other medicines to treat or prevent kidney failure and shock
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outcome depends on how severe the reaction is. The disorder may disappear without problems. Or, it may be severe and life threatening.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Tell your health care provider if you are having a blood transfusion and you have had a reaction before.
Prevention
Donated blood is put into ABO and Rh groups to reduce the risk for transfusion reaction.
Before a transfusion, recipient and donor blood are tested (cross-matched) to see if they are compatible. A small amount of donor blood is mixed with a small amount of recipient blood. The mixture is checked under a microscope for signs of antibody reaction.
Before the transfusion, your provider will usually check again to make sure you are receiving the right blood.
Gallery
References
Hall JE, Hall ME. Blood types; transfusion; and tissue and organ transplantation. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, eds. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 36.
Savage W. Transfusion reactions to blood and cell therapy products. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 119.
Shaz BH, Hillyer CD. Transfusion medicine. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 167.