Eyes - bulging
Definition
Bulging eyes is the abnormal protrusion (bulging out) of one or both eyeballs.
Alternative Names
Protruding eyes; Exophthalmos; Proptosis; Bulging eyes
Considerations
Prominent eyes may be a family trait. But prominent eyes are not the same as bulging eyes. Bulging eyes should be checked by a health care provider.
Bulging of one eye, especially in a child, can be a very serious sign. It should be checked right away.
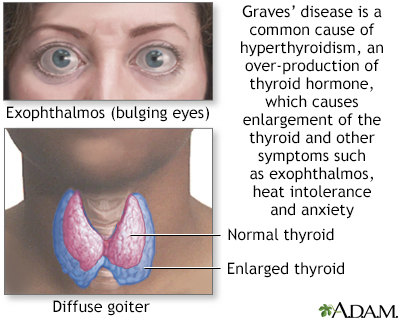
Hyperthyroidism (particularly Graves disease) is the most common medical cause of bulging eyes. With this condition, the eyes do not blink often and seem to have a staring quality.
Normally, there should be no visible white between the top of the iris (the colored part of the eye) and the upper eyelid. Seeing white in this area most often is a sign that the eye is bulging.
Because eye changes most often develop slowly, family members may not notice it until the condition is fairly advanced. Photos often draw attention to the bulging when it may have gone unnoticed before.
Causes
Causes may include:
- Glaucoma
- Graves disease
- Hemangioma
- Histiocytosis
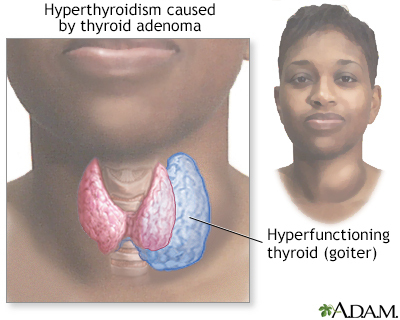
- Hyperthyroidism
- Leukemia
- Neuroblastoma
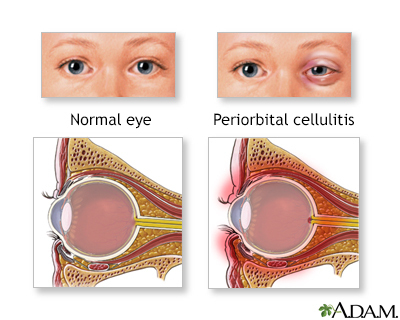
- Orbital cellulitis or periorbital cellulitis
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
Home Care
The cause needs to be treated by a provider. Because bulging eyes can cause a person to be self-conscious, emotional support is important.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have bulging eyes and the cause has not yet been diagnosed.
- Bulging eyes are accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain or fever.
The provider will ask about your medical history and do a physical exam.
Some questions you may be asked include:
- Are both eyes bulging?
- When did you first notice bulging eyes?
- Is it getting worse?
- What other symptoms do you have?
A slit-lamp examination may be done. Blood testing for thyroid disease may be done.
Treatments depend on the cause. Artificial tears may be given to lubricate the eye to protect its surface (cornea).
Gallery
References
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 395.
McNab AA. Proptosis at different ages. In: Lambert SR, Lyons CJ, eds. Taylor and Hoyt's Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 96.
Olson J. Medical ophthalmology. In: Ralston SH, Penman ID, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 27.
