Definition
Endoscopy is a way of looking inside the body using a flexible tube that has a small camera and light on the end of it. This instrument is called an endoscope.
Small instruments can be inserted through an endoscope and used to:
- Look more closely at an area inside the body
- Take samples of abnormal tissues (biopsy)
- Treat certain diseases
- Remove tumors
- Stop bleeding
- Remove foreign bodies (such as food stuck in the esophagus, the tube that connects your throat to your stomach)
How the Test is Performed
An endoscope is passed through a natural body opening or small cut. There are many types of endoscopes. Each one is named according to the organs or areas they are used to examine.
How to Prepare for the Test
Preparation for the procedure varies depending on the test. For example, there is no preparation needed for anoscopy. But a special diet and laxatives are needed to prepare for a colonoscopy. Follow your health care provider's instructions.
How the Test will Feel
All of these tests may cause discomfort or pain. Some are done after sedatives and pain medicines are given. Check with your provider about what to expect.
Why the Test is Performed
Each endoscopy test is done for different reasons. Endoscopy is most often used to examine and treat parts of the digestive tract, such as:
- Anoscopy views the inside of the anus, the very lowest part of the colon.
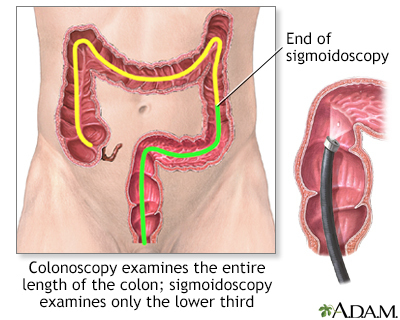
- Colonoscopy views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum.
- Enteroscopy views the inside of the small intestine (small bowel).
- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) views the biliary tract, small tubes that drain the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas.
- Sigmoidoscopy views the inside of the lower part of the colon called the sigmoid colon and rectum.
- Upper endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or EGD) views the inside of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine (called the duodenum).
- Bronchoscopy is used to look in the airways (windpipe, or trachea) and lungs.
- Cystoscopy is used to view the inside of the bladder. The scope is passed through the opening of the urethra.
- Laparoscopy is used to look directly at the ovaries, appendix, or other abdominal organs. The scope is inserted through small surgical cuts in the pelvic or belly area. Tumors or organs in the abdomen or pelvis can be removed.
- Arthroscopy is used to look directly in the joints, such as the knee. The scope is inserted through small surgical cuts around the joint. Problems with bones, tendons, ligaments can be treated.
Risks
Each endoscopy test has its own risks. Your provider will explain the risks to you before the procedure.
References
Phillips BB. General principles of arthroscopy. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 49.
Raymond L, Lentz GM. Endoscopy in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 10.
Sugumar A, Vargo JJ. Preparation for and complications of gastrointestinal endoscopy. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 42.
Yu DH, Feller-Kopman D. Tracheobronchial endoscopy. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 71.