Drug-induced thrombocytopenia
Definition
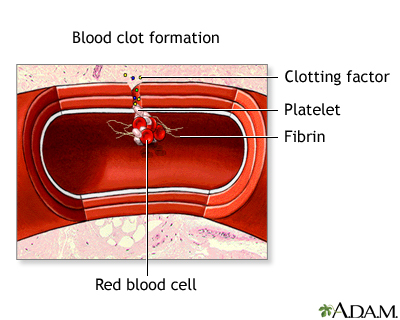
Thrombocytopenia is any disorder in which there are not enough platelets. Platelets are cells in the blood that help the blood clot. A low platelet count makes bleeding more likely.
When medicines or drugs are the causes of a low platelet count, it is called drug-induced thrombocytopenia.
Alternative Names
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia; Immune thrombocytopenia - drug
Causes
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia occurs when certain medicines destroy platelets or interfere with the body's ability to make enough of them.
There are two types of drug-induced thrombocytopenia: immune and nonimmune.
If a medicine causes your body to produce antibodies, which seek and destroy your platelets, the condition is called drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia. Heparin, a blood thinner, is the most common cause of drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia.
If a medicine prevents your bone marrow from making enough platelets, the condition is called drug-induced nonimmune thrombocytopenia. Chemotherapy drugs and a seizure medicine called valproic acid may lead to this problem.
Other medicines that cause drug-induced thrombocytopenia include:
- Furosemide
- Gold, used to treat arthritis
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Penicillin
- Quinidine
- Quinine
- Ranitidine
- Sulfonamides
- Linezolid and other antibiotics
- Statins
Symptoms
Decreased platelets may cause:
Treatment
The first step is to stop using the medicine that is causing the problem.
For people who have life-threatening bleeding, treatments may include:
- Immunoglobulin therapy (IVIG) given through a vein
- Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis)
- Platelet transfusions
- Corticosteroid medicine
Possible Complications
Bleeding can be life threatening if it occurs in the brain or other organs.
A pregnant woman who has antibodies to platelets may pass the antibodies to the baby in the womb.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your healthcare provider if you have unexplained bleeding or bruising and are taking medicines, such as the ones mentioned above under Causes.
Gallery
References
Abrams CS. Thrombocytopenia. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 163.
Warkentin TE. Thrombocytopenia caused by platelet destruction, hypersplenism, or hemodilution. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 132.