Definition
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a rate that is much too fast. The liver processes the fat into a fuel called ketones, which causes the blood to become acidic.
Alternative Names
DKA; Ketoacidosis; Diabetes - ketoacidosis
Causes
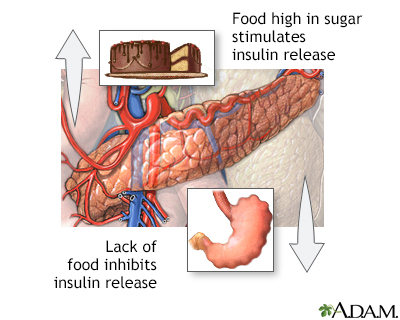
DKA happens when the signal from insulin in the body is so low that:
-
Glucose (blood sugar) can't go into cells to be used as a fuel source.
- The liver makes a huge amount of blood sugar.
- Fat is broken down too rapidly for the body to process.
The fat is broken down by the liver into a fuel called ketones. Ketones are normally produced by the liver when the body breaks down fat after it has been a long time since your last meal. These ketones are normally used by the muscles and the heart. When ketones are produced too quickly and build up in the blood, they can be toxic by making the blood acidic. This condition is known as ketoacidosis.
DKA is sometimes the first sign of type 1 diabetes in people who have not yet been diagnosed. It can also occur in someone who has already been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Infection, injury, a serious illness, missing doses of insulin shots, or the stress of surgery can lead to DKA in people with type 1 diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but it is less common and less severe. It is usually triggered by prolonged uncontrolled blood sugar, missing doses of medicines, or a severe illness or infection.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of DKA can include:
Exams and Tests
Ketone testing may be used in type 1 diabetes to screen for early ketoacidosis. The ketone test is usually done using a urine sample or a blood sample.
Ketone testing is usually done when DKA is suspected:
- Most often, urine testing is done first.
- If the urine is positive for ketones, most often a ketone called beta-hydroxybutyrate is measured in the blood. This is the most common ketone measured. The other main ketone is acetoacetate.
Other tests for ketoacidosis include:
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to correct the high blood sugar level with insulin. Another goal is to replace fluids lost through urination, loss of appetite, and vomiting if you have these symptoms.
If you have diabetes, it is likely your health care provider told you how to spot the warning signs of DKA. If you think you have DKA, test for ketones using urine strips. Some glucose meters can also measure blood ketones. If ketones are present, call your provider right away. Do not delay. Follow any instructions you are given.
It is likely that you will need to go to the hospital. There, you will receive insulin, fluids, and other treatment for DKA. Then providers will also search for and treat the cause of DKA, such as an infection.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people respond to treatment within 24 hours. Sometimes, it takes longer to recover.
If DKA is not treated, it can lead to severe illness or death.
Possible Complications
Health problems that may result from DKA include any of the following:
When to Contact a Medical Professional
DKA is a medical emergency. Call your provider if you notice symptoms of DKA.
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you or a family member with diabetes has any of the following:
- Decreased consciousness
- Fruity breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Trouble breathing
Prevention
If you have diabetes, learn to recognize the signs and symptoms of DKA. Know when to test for ketones, such as when you are sick.
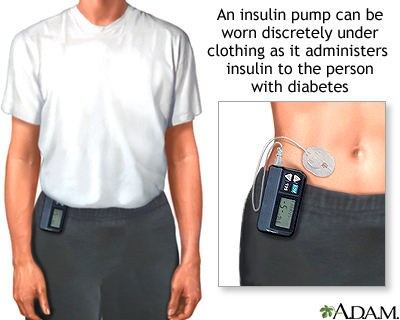
If you use an insulin pump, check often to see that insulin is flowing through the tubing. Make sure the tube is not blocked, kinked or disconnected from the pump.
References
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S17-S38. PMID: 34964875 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34964875/.
Atkinson MA, Mcgill DE, Dassau E, Laffel L. Type 1 diabetes. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 36.
Maloney GE, Glauser JM. Diabetes mellitus and disorders of glucose homeostasis. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 118.