Cryptococcosis
Definition
Cryptococcosis is infection with the fungi Cryptococcus neoformans or Cryptococcus gattii.
Alternative Names
C. neoformans var. neoformans infection; C. neoformans var. gatti infection; C. neoformans var. grubii infection
Causes
C neoformans and C gattii are the fungi that cause this disease. Infection with C neoformans is seen worldwide. Infection with C gattii has mainly been seen in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States, British Columbia in Canada, Southeast Asia, and Australia. In the United States, sporadic cases have been seen in many states including Washington, Oregon, California, Idaho, Hawaii, Georgia, Rhode Island, and Florida. Cryptococcus is the most common fungus that causes serious infection worldwide.
Both types of fungi are found in soil. If you breathe the fungus in, it infects your lungs. The infection may go away on its own, remain in the lungs only, or spread throughout the body (disseminate). C neoformans infection is most often seen in people with a weak immune system, such as those who:
- Are infected with HIV/AIDS
- Take corticosteroid medicines
- Cancer
- Are on chemotherapy medicines for cancer
- Have Hodgkin disease
- Have had an organ transplant
C gattii may affect people with normal immune system.
C neoformans is the most common life-threatening cause of fungal infection in people with HIV/AIDS.
People between 20 to 40 years of age are the most common age group that has this infection.
Symptoms
The infection may spread to the brain in people who have a weakened immune system. Neurological (brain) symptoms start slowly. Most people have swelling and irritation of the brain and spinal cord when they are diagnosed. Symptoms of brain infection may include:
- Fever and headache
- Neck stiffness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision or double vision
- Confusion
The infection can also affect the lungs and other organs. Lung symptoms may include:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Cough
- Chest pain
Other symptoms may include:
- Bone pain or tenderness of the breastbone
- Fatigue
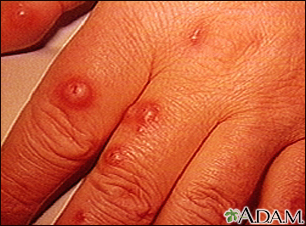
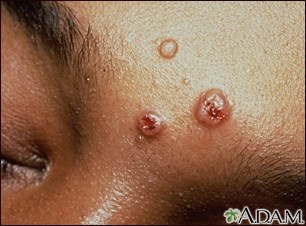
- Skin rash, including pinpoint red spots (petechiae), ulcers, or other skin lesions
- Sweating -- unusual, excessive at night
- Swollen glands
- Unintentional weight loss
People with a healthy immune system may have no symptoms at all.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms and travel history. The physical exam may reveal:
- Abnormal breath sounds
- Fast heart rate
- Fever
- Mental status changes
- Stiff neck
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood culture to differentiate between the two fungi
- CT scan of the head
- Sputum culture and stain
- Lung biopsy
- Bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage
- Spinal tap to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture and other tests to check for signs of infection
- Chest x-ray
- Cryptococcal antigen test (looks for a certain molecule that is shed from the cell wall of the Cryptococcus fungus into the bloodstream or CSF)
Treatment
Fungal medicines are prescribed for people infected with cryptococcus.
Medicines include:
- Amphotericin B (can have severe side effects)
- Flucytosine
- Fluconazole
Outlook (Prognosis)
Central nervous system involvement often causes death or leads to permanent damage.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of cryptococcosis, especially if you have a weakened immune system.
Gallery
References
Kauffman CA, Chen SC-A. Cryptococcosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 317.
Perfect JR. Cryptococcosis (Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 262.
Robles WS, Ameen M. Cryptococcosis. In: Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Murrell DF, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 49.
