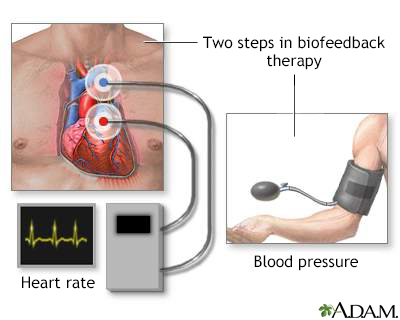
Definition
Biofeedback is a technique that measures bodily functions and gives you information about them in order to help train you to control them.
Information
Biofeedback is most often based on measurements of:
- Blood pressure
- Brain waves (EEG)
- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Muscle tension
- Skin conductivity of electricity
- Skin temperature
By watching these measurements, you can learn how to change these functions by relaxing or by holding pleasant images in your mind.
Patches, called electrodes, are placed on different parts of your body. They measure your heart rate, blood pressure, or other function. A monitor displays the results. A tone or other sound may be used to let you know when you have reached a goal or certain state.
Your health care provider will describe a situation and guide you through relaxation techniques. The monitor lets you see how your heart rate and blood pressure change in response to being stressed or remaining relaxed.
Biofeedback teaches you how to control and change these bodily functions. By doing so, you feel more relaxed or more able to cause specific muscle relaxation processes. This may help treat conditions such as:
References
Deutsch JK, Haas DJ. Complementary, alternative medicine, and integrative medicine. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 131.
Hecht FM. Complementary, alternative, and integrative medicine. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 34.
Hosey M, McWhorter JW, Wegener ST. Psychologic interventions for chronic pain. In: Benzon HT, Raja SN, Liu SS, Fishman SM, Cohen SP, eds. Essentials of Pain Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 59.